
Published: August 21st, 2024 • Last Updated: August 21st, 2024
Author: Ross Taylor on AskRoss.ca
How the Bank of Canada’s 2% Inflation Target Affects Your Housing Expenses
Let’s talk about inflation. Inflation occurs when prices for goods and services go up over time. The Bank of Canada tries to keep inflation around 2% each year. They call this their “inflation target.”
Why 2%? Well, when inflation is low and steady like that, it helps our economy run smoothly. People and businesses can make long-term plans without worrying about big price swings.

What is shelter inflation?
One of the main drivers behind this decline has been the slowdown in shelter prices. Shelter inflation refers to the increase in prices for housing-related expenses over time.
This includes things like:
- Rent payments
- Mortgage interest costs
- Property taxes
- Utilities (like electricity and water)
When we talk about shelter inflation easing, it means that these housing costs are rising at a slower pace than before.
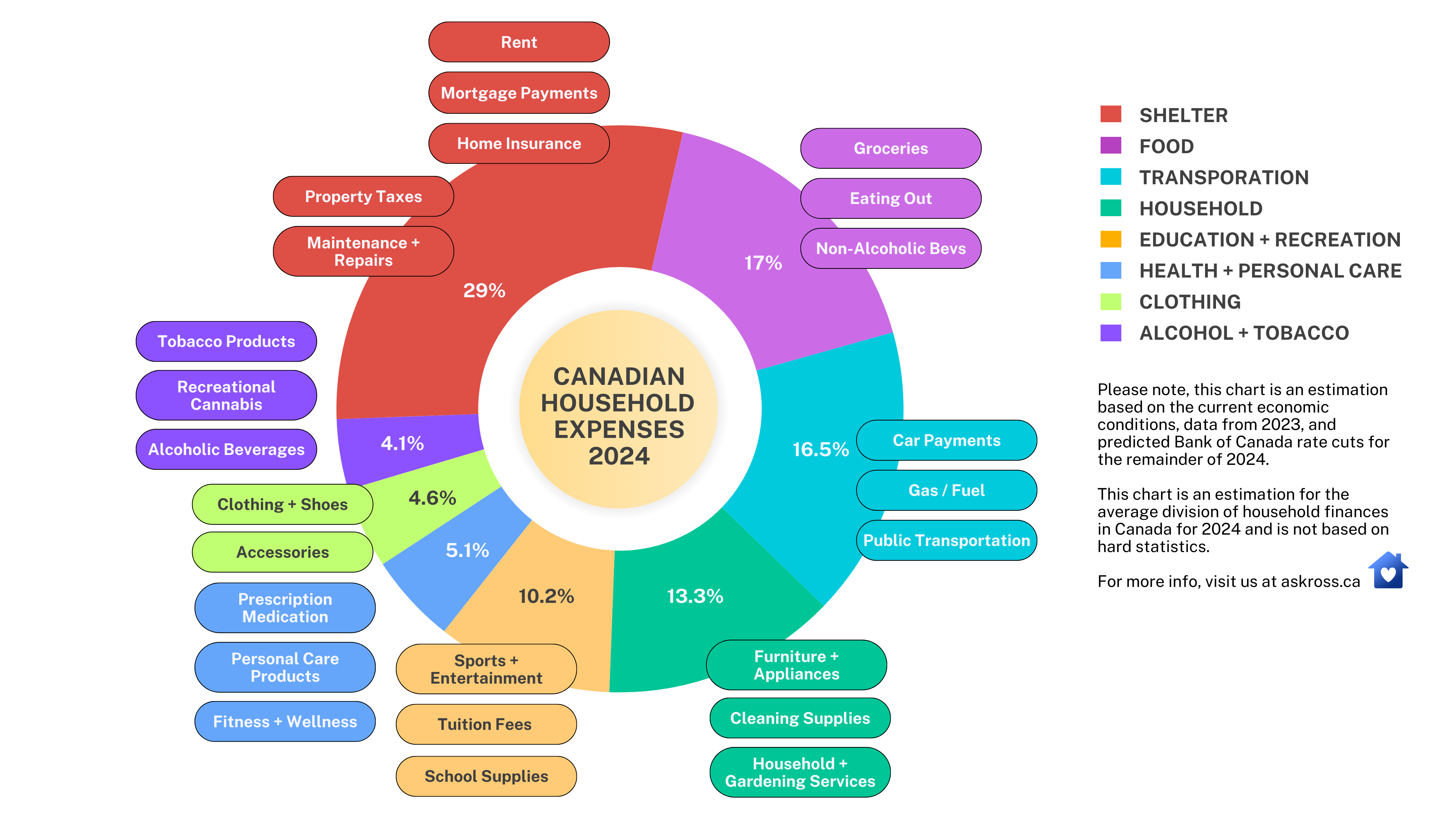
The average division of finances in Canadian Households in 2024
We’ve put together this handy chart to give you a clear picture of how the average Canadian household might spend their money in 2024. Please note that the data in this chart is an estimation based on the current economic conditions, data from 2023, and the forecasted Bank of Canada rate cuts for the remainder of 2024. For more info on the Bank of Canada’s upcoming rate cuts, visit our article here.

Why is shelter inflation cooling off?
The main reason shelter inflation is slowing down is because mortgage interest rates have come down quite a bit from their peak. Here’s what happened:
- A year ago, mortgage rates were much higher than today, coming in routinely over 6% for all term lengths. That means people were paying a lot more in interest on their home loans.
- In July 2024, shelter inflation was 5.7%, down from 6.2% in June. So the pace of increase in housing costs is moderating.
- The cost to rent in major cities has also declined year over year in specific cities like Vancouver and Toronto, which are traditionally expensive markets. However, provinces like Alberta experienced rapid rent increases, with rates growing by as much as 15.6% year-over-year.
So, in a nutshell, lower mortgage rates are helping to cool off shelter inflation. When people pay less in mortgage interest, it helps slow down the overall increase in housing costs.
Why does this matter?
Shelter inflation is a big deal because housing is the largest expense for most Canadians. When shelter inflation is high, it eats up more of people’s incomes and leaves less money for basic necessities. We’ve all felt the pain of ever-climbing grocery prices. But when shelter inflation eases, it means housing costs will take up a smaller chunk of household budgets.
This cooling off in shelter prices is one of the main reasons why overall inflation has been coming down in recent months. It’s a positive sign that the cost of living is starting to moderate, which is good news for Canadian families.

How does high inflation hurt Canadians?
When inflation is too high, it’s tough on everyone, especially folks with low or fixed incomes. Your money doesn’t stretch as far at the grocery store or the gas pump.
Plus, when prices are rising quickly, businesses raise their prices more often. Consumers start to expect higher prices, so they don’t shop around for deals as much. This can make inflation even worse.
The Bank of Canada’s next move
The monthly change in the rate of inflation, largely driven by rising gas prices, remains above the pace needed to achieve the Bank of Canada’s 2% inflation target. However, this is unlikely to deter the Bank of Canada from implementing another rate cut in two weeks. Here’s why:
- The ongoing drop in inflation aligns well with the Bank’s forecasts.
- This bolsters the likelihood of a further rate reduction.
- Many analysts anticipate the central bank will lower its key interest rate by 0.25% at its upcoming meeting on September 4.
- I would not be surprised at all if the Bank also cuts rates in October and December. There is a sense that the markets are fully primed for this.
For a deeper dive into what the Bank of Canada’s recent rate cut means for Canadians, I’ve put together a comprehensive Q&A article. In it, I cover everything from how the rate cut impacts variable-rate mortgage holders to the pros and cons of switching to a fixed-rate mortgage in the current economic climate.
I also share my insights on what we can expect for future rate changes based on expert predictions for the remainder of 2024 and going into 2025.
Check out the full article here: Bank of Canada Rate Cut July 2024 Q&A: What It Means for Canadians – Everything You Need to Know – ASK ROSS

The Solution: Slowing down spending
To get inflation back to normal, we needed to slow down spending in the economy. This will give supply a chance to catch up with demand.
One way the Bank of Canada did this was by raising interest rates. When rates go up, it costs more to borrow money, so Canadians and businesses tend to spend less. Over time, this helps bring inflation down, and that’s exactly where we are today. After two-plus years of brutal high inflation, the BoC’s rate policy has had its desired effect.
Key Takeaway
Even though inflation has dipped a bit, it’s still a touch above where the Bank of Canada wants it to be. The Bank of Canada is committed to getting us back to that sweet spot of low, stable, and predictable inflation. Lower inflation and interest rates will spell opportunity for real estate buyers and homeowners.

Ross Taylor Mortgages
As always, we’re here to help. If you have any questions or want to consult with one of our award-winning mortgage professionals, book your free consultation today.
Get quick answers to your questions, no matter how difficult – 7 days a week.

 Apply For a Mortgage
Apply For a Mortgage